Page Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 I. What is Gingivitis in Dogs?
- 3 II. Symptoms of Gingivitis in Dogs
- 4 III. Stages of Gingivitis in Dogs
- 5 IV. Recognizing and Diagnosing Gingivitis in Dogs
- 6 V. Dog Gingivitis Treatment
- 7 Conclusion
- 8 FAQs
- 8.1 Part 1
- 8.1.1 1. How to treat gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.1.2 2. How to reverse gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.1.3 3. How to get rid of gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.1.4 4. How to prevent gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.1.5 5. How to cure gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.1.6 6. How to help gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.1.7 7. How to treat gingivitis in dogs at home?
- 8.1.8 8. What is gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.1.9 9. What does gingivitis look like in dogs?
- 8.1.10 10. What causes gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.1.11 11. How to fix gingivitis in dogs?
- 8.2 Part 2
- 8.2.1 1. How to treat dog gingivitis?
- 8.2.2 2. How to get rid of dog gingivitis?
- 8.2.3 3. How to cure dog gingivitis?
- 8.2.4 4. How to help dog gingivitis?
- 8.2.5 5. How to fix dog gingivitis?
- 8.2.6 6. What can I give my dog for gingivitis?
- 8.2.7 7. My dog has gingivitis, what can I do?
- 8.2.8 8. How to treat dog gingivitis at home?
- 8.2.9 9. How to help dog with gingivitis?
- 8.2.10 10. What to do for dog gingivitis?
- 8.2.11 11. How to take care dog teeth gingivitis?
- 8.2.12 12. What does dog gingivitis look like?
- 8.1 Part 1
Introduction
Gingivitis, a common dental condition among dogs, refers to inflammation of the gums caused by a buildup of plaque and bacteria. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to more serious oral health issues. In this blog post, we will explore the stages of gingivitis in dogs, its symptoms, causes, and effective treatment options.
I. What is Gingivitis in Dogs?
Gingivitis is a common dental condition that affects dogs, just as it does humans. It refers to the inflammation of the gums, which can be caused by a buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Proper dental care is crucial for canines, as poor oral hygiene can lead to various dental problems, including gingivitis.
Gingivitis initially starts as a mild inflammation of the gums. If left untreated, it can progress and damage the supporting structures of the teeth, including the tooth root and the surrounding bone. This can cause pain, discomfort, and eventual tooth loss for the affected dog.
What Causes Gingivitis in Dogs?
- Plaque buildup and bacterial infections are major contributors to gingivitis in dogs. When plaque, which is a sticky film composed of bacteria, mucus, and food particles, is not adequately removed, it can harden into tartar. Tartar provides a perfect breeding ground for bacteria and promotes gum inflammation and infection. This can progress to periodontal disease in dogs, a more severe form of Gum disease, if not addressed promptly.
- Some dog breeds are more susceptible to developing gingivitis due to their anatomy or genetics. Breeds with crowded or misaligned teeth, narrow mouths, or short noses are more prone to oral health issues.
- Certain genetic factors can make some dogs more predisposed to dental problems, including gum disease.
- The impact of diet on oral health should not be underestimated. Feeding dogs a diet high in carbohydrates and sugars can contribute to plaque formation and increase the likelihood of developing gum disease.
- A lack of appropriate chewing options, such as dental chews or toys, can hinder the natural cleaning process of a dog’s teeth and gums.
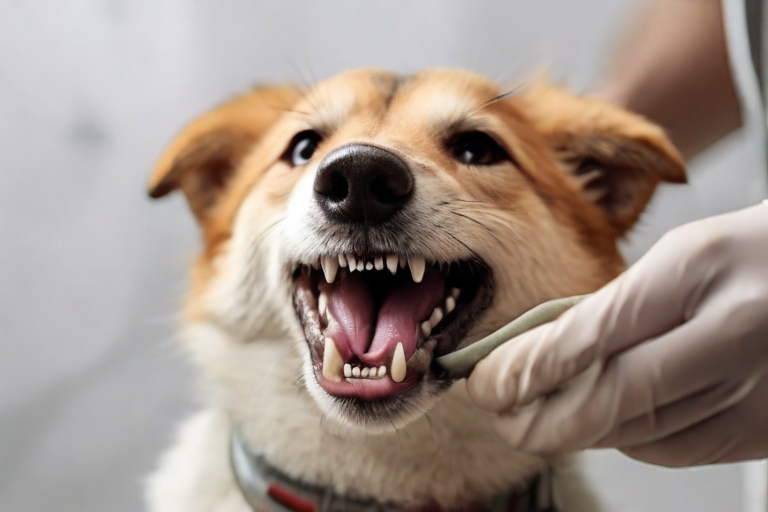
II. Symptoms of Gingivitis in Dogs
Recognizing the symptoms of gingivitis in dogs is crucial for early intervention. Some common signs include red and swollen gums, bleeding gums during brushing or chewing, bad breath (halitosis), and discomfort or reluctance to eat. Owners may also notice visible tartar or plaque buildup on their dog’s teeth. Additionally, changes in behavior or mood, such as increased irritability or depression, can be indicators of dental issues.
III. Stages of Gingivitis in Dogs
Stage 1: Mild Gingivitis on Dogs
In the initial stage of gingivitis, mild inflammation of the gums is observed. The gums may appear slightly red and swollen, and there may be minimal plaque buildup. Plaque, a sticky film that forms on the teeth, contains bacteria that can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation. However, at this stage, the condition is reversible with appropriate dental care. Regular and thorough brushing and flossing, along with professional dental cleanings, can help eliminate the plaque and restore gum health.
Stage 2: Moderate Gingivitis
As gingivitis progresses, the signs become more noticeable. The gums become increasingly red and swollen, and there is a moderate buildup of plaque. This buildup can eventually harden into tartar, which cannot be removed by regular brushing alone. As a result, the gums may start to recede, exposing the roots of the teeth. This can cause tooth sensitivity and discomfort. It is crucial to seek dental treatment at this stage to prevent further damage and complications.
Stage 3: Severe Gingivitis
When left untreated, gingivitis can reach the severe stage, posing a significant risk to oral health. The gum inflammation becomes pronounced, and there is extensive plaque and tartar accumulation. These deposits can create pockets between the teeth and gums, allowing bacteria to thrive and further damage the supporting structures of the teeth. If left unaddressed, severe gingivitis can lead to periodontitis, a more advanced stage of Gum disease. This can result in tooth loss, bone loss, and an increased risk of systemic health conditions such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
IV. Recognizing and Diagnosing Gingivitis in Dogs
Recognizing and diagnosing gingivitis in dogs requires regular dental check-ups and comprehensive oral examinations performed by a veterinarian. These examinations involve evaluating the overall condition of the gums, teeth, and mouth for any signs of inflammation, infection, or other oral health issues. Along with visual examination, your veterinarian may recommend diagnostic tests, such as dental X-rays, to assess the extent of the disease.

V. Dog Gingivitis Treatment
While professional veterinary care should always be sought for serious dental issues, there are also some home remedies that can help manage and prevent gingivitis on dogs.
1. Professional Veterinary Care
When it comes to your dog’s dental health, it is crucial to consult a professional veterinarian. Regular dental cleanings, known as scaling and root planing, are an effective way to remove plaque and tartar buildup, preventing the progression of gingivitis on dogs.
In severe cases, damaged teeth may need to be extracted to prevent further complications. A veterinarian may also recommend antibacterial rinses or gels to control bacterial growth and maintain oral hygiene, additionally, discussing the cost considerations of professional dental care with your veterinarian will help you plan and prepare for any necessary treatments.
2. Dog Gingivitis Home Remedies
Apart from professional care, there are several home remedies that can assist in managing gingivitis in your dogs:
- Regular Brushing with Dog-Friendly Toothpaste:
Just like humans, dogs can benefit from regular toothbrushing. The first home remedy for gingivitis in dogs is using a toothbrush and toothpaste specifically formulated for dogs, gently brush your dog’s teeth at least two to three times a week. This helps remove plaque and tartar and reduces the risk of gingivitis on dogs. - Dental Chews or Specialized Treats:
Dental chews and treats designed to promote oral health can be effective in preventing and managing gingivitis. These products contain ingredients that help remove plaque and massage the gums, promoting good oral hygiene. - Mouth Rinses or Water Additives:
Mouth rinses or water additives formulated for dogs can help reduce plaque and bacteria in their mouths. These products are easy to use and can be added to your dog’s water bowl, providing an ongoing defense against gingivitis. - Neem Oil for Natural Antibacterial Properties:
Neem oil for dog gingivitis, derived from the neem tree, possesses natural antibacterial properties that can help combat gingivitis. Dilute neem oil with water and apply it to your Dog’s gums using a soft brush or cotton swab. Ensure your dog doesn’t lick it off immediately.
3. Preventive Measures for Gingivitis
1. Nutritional considerations and dental-friendly diets
A well-balanced diet plays a significant role in preventing dental problems, including gingivitis, in pets. Providing your pet with high-quality pet food that promotes dental health can improve their overall oral hygiene. Look for specially formulated pet foods that have additives such as enzymes or plaque-fighting ingredients that promote dental health
2. Proper oral hygiene routine
Just like humans, pets also require regular oral care to maintain healthy teeth and gums. Establishing a proper oral hygiene routine is essential in preventing gingivitis. Here are a few key steps to include in your pet’s routine:
- Brushing: Regular brushing is a fundamental aspect of oral care. Use a pet-specific toothbrush and toothpaste and gently brush your pet’s teeth in a circular motion. Start slow and gradually increase the time as your pet becomes more comfortable. Aim for daily brushing, but even a few times a week can make a significant difference.
- Mouth rinses: Using pet-friendly mouth rinses or dental sprays can help reduce plaque and freshen your pet’s breath. Consult with your veterinarian to select the most suitable product based on your pet’s specific needs.
- Dental wipes: For pets that are not comfortable with brushing, dental wipes can be a helpful alternative. These wipes are designed to remove food particles and reduce plaque buildup. Gently rub the wipes along your pet’s gum line and teeth.
Conclusion
Gingivitis in dogs is a common condition that should not be overlooked. By understanding its stages, symptoms, and causes, dog owners can take proactive steps to prevent and treat this oral health issue. With regular veterinary care, proper dental hygiene, and the use of appropriate treatment options, dogs can maintain healthy gums and a bright smile throughout their lives. Remember, your dog’s oral health is essential for his overall well-being and quality of life.
FAQs
Part 1
1. How to treat gingivitis in dogs?
Treating gingivitis in dogs usually involves a combination of professional dental care and at-home oral hygiene practices. Your veterinarian may recommend a dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup, along with any necessary dental procedures such as tooth extraction or periodontal treatment. At home, regular tooth brushing with a dog-friendly toothpaste and providing dental chews can help maintain your dog’s oral health.
2. How to reverse gingivitis in dogs?
While it’s not always possible to reverse gingivitis completely, it can be managed and prevented with proper dental care. Regular veterinary check-ups, professional dental cleanings, and at-home oral hygiene practices such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews can help keep your dog’s gums healthy and prevent gingivitis from worsening.
3. How to get rid of gingivitis in dogs?
Getting rid of gingivitis in dogs requires a combination of professional dental care and ongoing at-home oral hygiene practices. Your veterinarian may recommend a dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup, along with any necessary dental procedures. At home, regular tooth brushing, providing dental chews, and feeding a balanced diet can help prevent gingivitis from recurring.
4. How to prevent gingivitis in dogs?
Preventing gingivitis in dogs starts with good oral hygiene practices. Regular tooth brushing with a dog-friendly toothpaste and toothbrush, providing dental chews or toys, and feeding a balanced diet can all help prevent plaque and tartar buildup that can lead to gingivitis. Additionally, regular veterinary check-ups and professional dental cleanings can help catch and address any oral health issues early.
5. How to cure gingivitis in dogs?
While gingivitis in dogs can be managed and prevented with proper dental care, it’s not always possible to cure it completely. However, with regular veterinary check-ups, professional dental cleanings, and ongoing at-home oral hygiene practices, you can help keep your dog’s gums healthy and prevent gingivitis from worsening.
6. How to help gingivitis in dogs?
To help your dog with gingivitis, it’s important to prioritize their dental health. This includes regular veterinary check-ups and professional dental cleanings, as well as at-home oral hygiene practices such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews. Additionally, feeding a balanced diet and avoiding excessive treats or table scraps can help prevent plaque and tartar buildup that can contribute to gingivitis.
7. How to treat gingivitis in dogs at home?
While professional dental care is crucial for treating gingivitis in dogs, there are some things you can do at home to help. Regular tooth brushing with a dog-friendly toothpaste and toothbrush, providing dental chews or toys designed to promote dental hygiene, and feeding a balanced diet can all contribute to maintaining your dog’s oral health and preventing gingivitis.
8. What is gingivitis in dogs?
Gingivitis in dogs is inflammation of the gums caused by plaque and tartar buildup. It is a common dental problem in dogs and, if left untreated, can lead to more severe periodontal disease and tooth loss. Gingivitis can cause symptoms such as red, swollen, or bleeding gums, bad breath, and changes in eating or chewing habits.
9. What does gingivitis look like in dogs?
Gingivitis in dogs can present with symptoms such as red, swollen, or bleeding gums, bad breath, tartar buildup on the teeth, and changes in eating or chewing habits. In advanced cases, gum recession, loose teeth, and oral pain may also occur. If you notice any of these signs, it’s essential to consult with your veterinarian for proper diagnosis and treatment.
10. What causes gingivitis in dogs?
Gingivitis in dogs is primarily caused by plaque and tartar buildup on the teeth, which can irritate the gums and lead to inflammation. Other factors such as poor oral hygiene, genetics, age, diet, and underlying health conditions can also contribute to the development of gingivitis. Regular dental care and preventive measures can help reduce the risk of gingivitis in dogs.
11. How to fix gingivitis in dogs?
Fixing gingivitis in dogs requires a multi-faceted approach that includes professional dental care and at-home oral hygiene practices. Your veterinarian may recommend a dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup, along with any necessary dental procedures such as tooth extraction or periodontal treatment. At home, regular tooth brushing and providing dental chews can help maintain your dog’s oral health and prevent gingivitis from recurring.
Part 2
1. How to treat dog gingivitis?
Treating dog gingivitis typically involves professional dental care provided by a veterinarian. This may include a thorough dental cleaning to remove plaque and tartar buildup, along with any necessary dental procedures such as tooth extraction or periodontal treatment. Your vet may also recommend antibiotics or other medications to address infection or inflammation.
2. How to get rid of dog gingivitis?
Getting rid of dog gingivitis requires a combination of professional dental care and ongoing home oral hygiene practices. Professional dental cleanings performed by a veterinarian can remove plaque and tartar buildup, while at-home dental care such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews can help maintain oral health between cleanings. In some cases, additional treatments or medications may be necessary to address advanced gingivitis or associated complications.
3. How to cure dog gingivitis?
Curing dog gingivitis is not always possible, but it can be managed and prevented with proper dental care. Professional dental cleanings, along with at-home oral hygiene practices such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews, can help prevent gingivitis from worsening. It’s important to work closely with your vet to develop a dental care plan tailored to your dog’s needs.
4. How to help dog gingivitis?
To help your dog with gingivitis, it’s essential to prioritize their dental health. This includes regular veterinary check-ups and professional dental cleanings, as well as at-home oral hygiene practices such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews. Additionally, feeding a balanced diet and avoiding excessive treats or table scraps can help prevent plaque and tartar buildup that can contribute to gingivitis.
5. How to fix dog gingivitis?
Fixing dog gingivitis requires a multi-faceted approach that includes professional dental care and ongoing home oral hygiene practices. Professional dental cleanings performed by a veterinarian can remove plaque and tartar buildup, while at-home dental care such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews can help maintain oral health between cleanings. It’s important to address gingivitis early to prevent it from progressing to more severe periodontal disease.
6. What can I give my dog for gingivitis?
To help manage gingivitis in dogs, your vet may recommend a combination of professional dental care and at-home oral hygiene practices. This may include regular dental cleanings, antibiotics or other medications to address infection or inflammation, and at-home dental care such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews. It’s important to follow your vet’s recommendations closely to ensure your dog’s oral health is properly maintained.
7. My dog has gingivitis, what can I do?
If your dog has gingivitis, it’s important to seek veterinary care promptly. Your vet can assess the severity of the condition and recommend appropriate treatment options, which may include professional dental cleaning, dental procedures such as tooth extraction or periodontal treatment, and medications to address infection or inflammation. Additionally, your vet can provide guidance on at-home oral hygiene practices to help manage gingivitis and promote your dog’s oral health.
8. How to treat dog gingivitis at home?
While professional dental care is essential for treating dog gingivitis, there are some steps you can take at home to support your pup’s oral health. Regular tooth brushing with a dog-friendly toothpaste, providing dental chews or toys designed to promote dental hygiene, and feeding a balanced diet can all help prevent and manage gingivitis. However, it’s essential to consult with your vet before attempting any home remedies to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your dog.
9. How to help dog with gingivitis?
To help your dog with gingivitis, it’s important to prioritize their dental health. This includes regular veterinary check-ups and professional dental cleanings, as well as at-home oral hygiene practices such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews. Additionally, feeding a balanced diet and avoiding excessive treats or table scraps can help prevent plaque and tartar buildup that can contribute to gingivitis.
10. What to do for dog gingivitis?
If your dog has gingivitis, the first step is to schedule a veterinary appointment for a thorough dental examination. Your vet can assess the extent of the gingivitis and recommend appropriate treatment options. This may include professional dental cleaning, dental procedures such as tooth extraction or periodontal treatment, and medications to address infection or inflammation. Additionally, your vet can provide guidance on at-home oral hygiene practices to help manage gingivitis and promote your dog’s oral health.
11. How to take care dog teeth gingivitis?
To take care of your dog’s teeth and manage gingivitis, it’s important to prioritize their dental health. This includes regular veterinary check-ups and professional dental cleanings, as well as at-home oral hygiene practices such as tooth brushing and providing dental chews. Additionally, feeding a balanced diet and avoiding excessive treats or table scraps can help prevent plaque and tartar buildup that can contribute to gingivitis.
12. What does dog gingivitis look like?
Dog gingivitis can present with symptoms such as red, swollen, or bleeding gums, bad breath, tartar buildup on the teeth, and changes in eating or chewing habits. In advanced cases, gum recession, loose teeth, and oral pain may also occur. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to consult with your vet for proper diagnosis and treatment.



[…] gum disease refers to an infection and inflammation of the gums, also known as Gingivitis. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontal disease, which affects the tissues and […]